What is fetal fibronectin?
Fetal fibronectin (also known as fFN) is a “glue-like” protein that bonds the baby to the uterus.
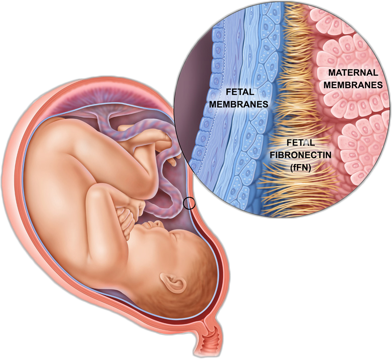
fFN holds the baby in place during its development and is usually not detectable in vaginal secretions during weeks 16 to 35 of gestation.
If fFN is “leaking” into the vagina during this time period, this can be a sign that your body is preparing to deliver early.1
How does the Rapid fFN® test work?
Getting tested is as simple as getting a pap test, except the Rapid fFN® test checks for the presence of fetal fibronectin.
If elevated levels of fFN are detected in your vaginal secretions between weeks 22 and 35, your body may be preparing to give birth prematurely.2
What does the Rapid fFN® test tell you?
The Rapid fFN® test is a highly reliable test that predicts your risk of going into labor in the next week or two. If you receive a negative result, it means that you have less than a 1% chance of delivering in the next two weeks.2 Your doctor, nurse or midwife uses your Rapid fFN® test results, along with your obstetric history and their clinical judgment to manage your care.
